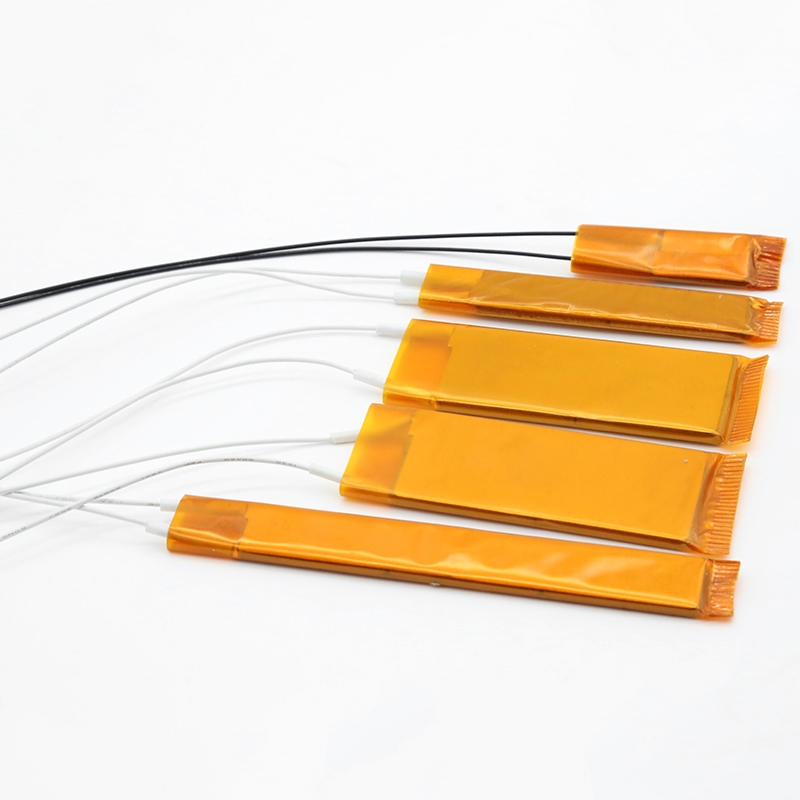
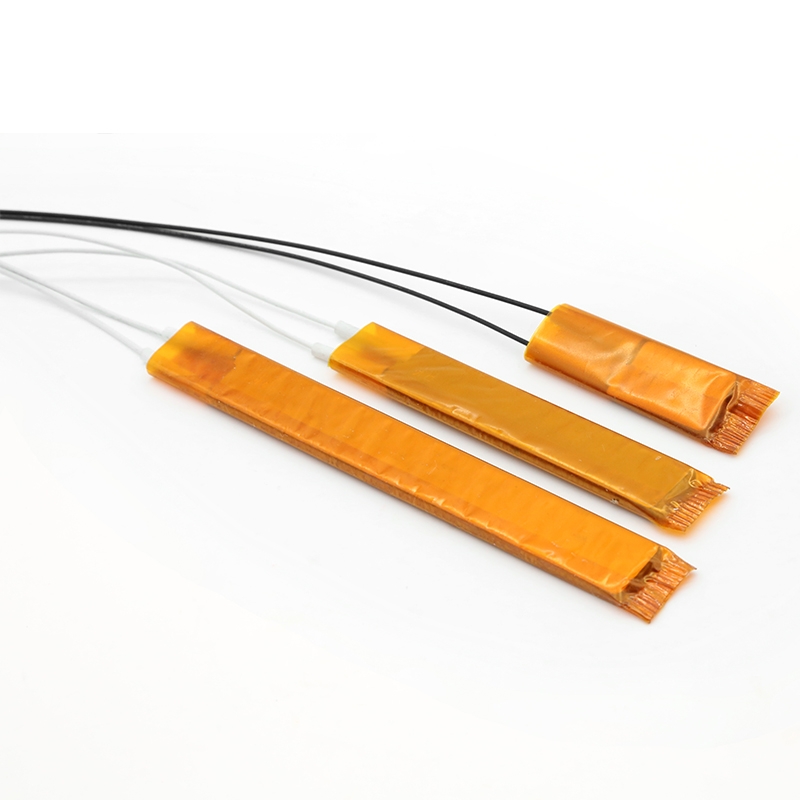
Description
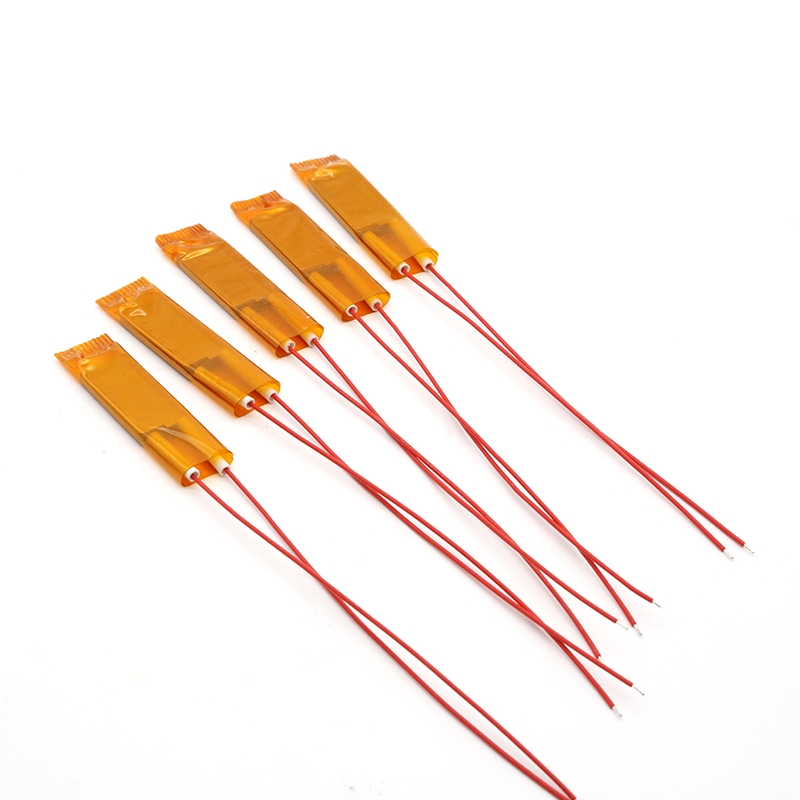
Polyimide (PI) Heating Films, often referred to as film heaters, are thin, flexible, and lightweight electric heating elements. They are constructed using a high-temperature polyimide film as both the substrate and the overlay, with an etched-foil heating circuit encapsulated in between. This advanced design makes them ideal for applications requiring precise, reliable heat in a minimal space and under demanding conditions.
Specification
|
Product Name |
PI metal thin film heating element |
| Size |
60x10mm or customized |
|
Heater body |
0.4±10% or customized |
|
Material |
PI |
| Voltage | 3.7V or customized |
|
Application |
Suitable for various low-pressure heating scenarios |








Feature
-
Exceptional Thinness and Flexibility: With a typical thickness of only 0.1 to 0.3 mm, these heaters can be easily bent and conform to complex or curved surfaces, ensuring efficient heat transfer.
-
Lightweight and Space-Saving: Their minimal weight and profile make them perfect for weight-sensitive and compact applications, such as in aerospace and portable electronics.
-
Rapid Thermal Response: The low thermal mass of the polyimide film and the thin heating element allow for very fast heat-up and cool-down times, enabling precise temperature control.
-
Excellent Temperature Uniformity: The photochemically etched foil circuit ensures even heat distribution across the entire heating surface, eliminating hot and cold spots.
-
High-Temperature Resistance: The polyimide material can withstand continuous operating temperatures typically up to 220°C, with some variants rated even higher, ensuring long-term stability and performance.
-
Chemical and Radiation Resistance: PI films are highly resistant to most chemicals, solvents, and radiation, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Application
In summary, Polyimide Heating Films represent a premium heating solution where conventional heaters are too bulky, rigid, or unreliable. Their unique combination of thinness, flexibility, rapid response, and high-performance under extreme conditions makes them the preferred choice for a wide range of industries. Common applications include thermal management in aerospace (de-icing, sensor heating), medical devices (diagnostic equipment, blood analyzers), consumer electronics (3D printer beds), and battery systems in electric vehicles. They offer engineers a reliable and efficient method to deliver precise heat exactly where it is needed.